Evolution of Operating Systems
Operating Systems have evolved in past years. It went through several changes before getting its original form. These changes in the operating system are known as the *evolution of operating systems*.OS improve itself with the invention of new technology. Basically , OS added the feature of new technology and making itself more powerful. Let us see the evolution of operating system year-wise in detail:
First Generation (1945-1955)
It is the beginning of the development of electronic computing systems which are substitutes for mechanical computing systems. Because of the drawbacks in mechanical computing systems like, the speed of humans to calculate is limited and humans can easily make mistakes. In this generation there is no operating system, so the computer system is given instructions which must be done directly.
Example − Type of operating system and devices used is Plug Boards.
Second Generation (1955-1965)
The Batch processing system was introduced in the second generation, where a job or a task that can be done in a series, and then executed sequentially. In this generation, the computer system is not equipped with an operating system, but several operating system functions exist like FMS and IBSYS.
Example − Type of operating system and devices used is Batch systems.
Third Generation (1965-1980)
The development of the operating system was developed to serve multiple users at once in the third generation. Here the interactive users can communicate through an online terminal to a computer, so the operating system becomes multi-user and multiprogramming.
Example − Type of operating system and devices used is Multiprogramming.
Fourth Generation (1980-Now)
In this generation the operating system is used for computer network where users are aware of the existence of computers that are connected to one another.
At this generation users are also comforted with a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which is an extremely comfortable graphical computer interface, and the era of distributed computing has also begun.
With the occurrence of new wearable devices like Smart Watches, Smart Glasses, VRGears, and others, the demand for conventional operating systems has also increased.
And, with the onset of new devices like wearable devices, which includes Smart Watches, Smart Glasses, VR gears etc, the demand for unconventional operating systems is also rising.
Example − Type of operating system and devices used is personal computers
Types of Operating Systems (OS)
An operating system is a well-organized collection of programs that manages the computer hardware. It is a type of system software that is responsible for the smooth functioning of the computer system.
Batch Operating System
In the 1970s, Batch processing was very popular. In this technique, similar types of jobs were batched together and executed in time. People were used to having a single computer which was called a mainframe.
In Batch operating system, access is given to more than one person; they submit their respective jobs to the system for the execution.
The system put all of the jobs in a queue on the basis of first come first serve and then executes the jobs one by one. The users collect their respective output when all the jobs get executed.
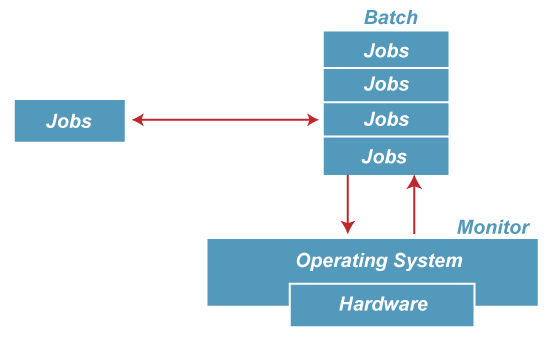
The purpose of this operating system was mainly to transfer control from one job to another as soon as the job was completed. It contained a small set of programs called the resident monitor that always resided in one part of the main memory. The remaining part is used for servicing jobs.
Advantages of Batch OS
- The use of a resident monitor improves computer efficiency as it eliminates CPU time between two jobs.
Disadvantages of Batch OS
1. Starvation
Batch processing suffers from starvation.
For Example:
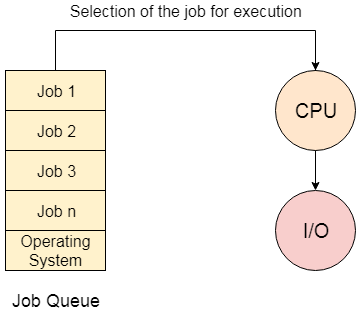
There are five jobs J1, J2, J3, J4, and J5, present in the batch. If the execution time of J1 is very high, then the other four jobs will never be executed, or they will have to wait for a very long time. Hence the other processes get starved.
2. Not Interactive
Batch Processing is not suitable for jobs that are dependent on the user's input. If a job requires the input of two numbers from the console, then it will never get it in the batch processing scenario since the user is not present at the time of execution.
Multiprogramming Operating System
Multiprogramming is an extension to batch processing where the CPU is always kept busy. Each process needs two types of system time: CPU time and IO time.
In a multiprogramming environment, when a process does its I/O, The CPU can start the execution of other processes. Therefore, multiprogramming improves the efficiency of the system.
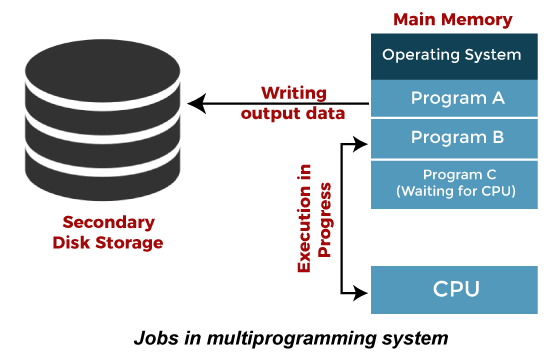
Advantages of Multiprogramming OS
- Throughout the system, it increased as the CPU always had one program to execute.
- Response time can also be reduced.
Disadvantages of Multiprogramming OS
- Multiprogramming systems provide an environment in which various systems resources are used efficiently, but they do not provide any user interaction with the computer system.
Multiprocessing Operating System
In Multiprocessing, Parallel computing is achieved. There are more than one processors present in the system which can execute more than one process at the same time. This will increase the throughput of the system.
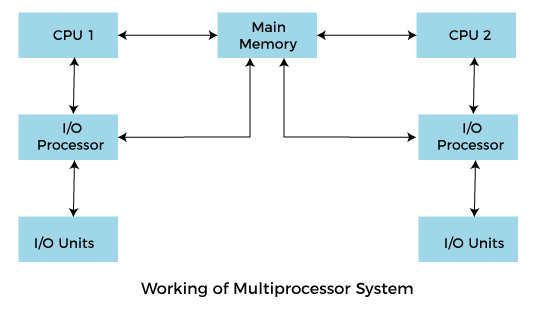
In Multiprocessing, Parallel computing is achieved. More than one processor present in the system can execute more than one process simultaneously, which will increase the throughput of the system.
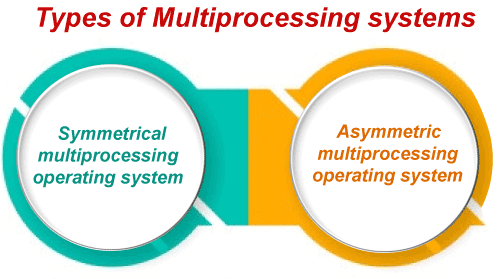
Advantages of Multiprocessing operating system:
- Increased reliability: Due to the multiprocessing system, processing tasks can be distributed among several processors. This increases reliability as if one processor fails, the task can be given to another processor for completion.
- Increased throughout: As several processors increase, more work can be done in less.
Disadvantages of Multiprocessing operating System
- Multiprocessing operating system is more complex and sophisticated as it takes care of multiple CPUs simultaneously.
Multitasking Operating System
The multitasking operating system is a logical extension of a multiprogramming system that enables multiple programs simultaneously. It allows a user to perform more than one computer task at the same time.
Advantages of Multitasking operating system
- This operating system is more suited to supporting multiple users simultaneously.
- The multitasking operating systems have well-defined memory management.
Disadvantages of Multitasking operating system
- The multiple processors are busier at the same time to complete any task in a multitasking environment, so the CPU generates more heat.
Network Operating System
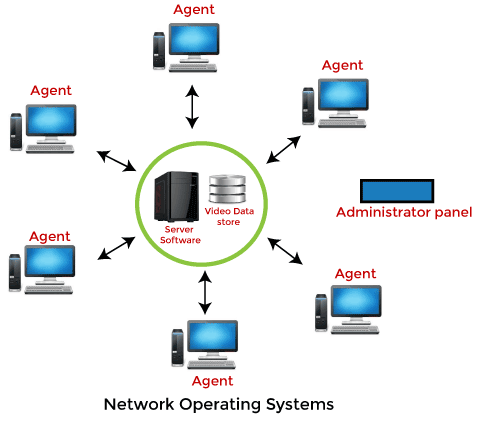
An Operating system, which includes software and associated protocols to communicate with other computers via a network conveniently and cost-effectively, is called Network Operating System.
Advantages of Network Operating System
- In this type of operating system, network traffic reduces due to the division between clients and the server.
- This type of system is less expensive to set up and maintain.
Disadvantages of Network Operating System
- In this type of operating system, the failure of any node in a system affects the whole system.
- Security and performance are important issues. So trained network administrators are required for network administration.
Real Time Operating System
In Real-Time Systems, each job carries a certain deadline within which the job is supposed to be completed, otherwise, the huge loss will be there, or even if the result is produced, it will be completely useless.
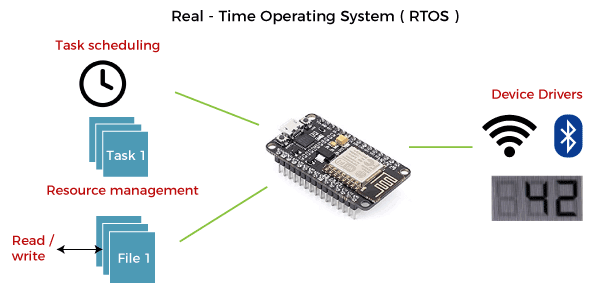
The Application of a Real-Time system exists in the case of military applications, if you want to drop a missile, then the missile is supposed to be dropped with a certain precision.
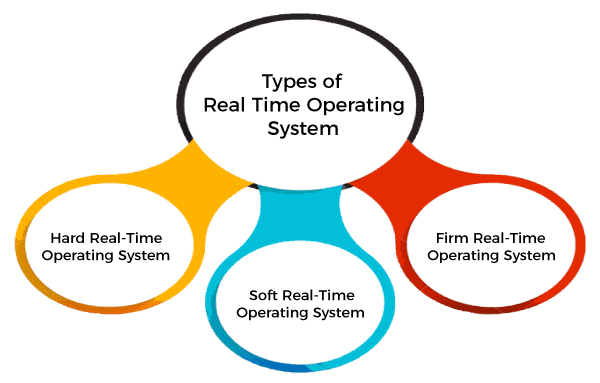
Advantages of Real-time operating system:
- Easy to layout, develop and execute real-time applications under the real-time operating system.
- In a Real-time operating system, the maximum utilization of devices and systems.
Disadvantages of Real-time operating system:
- Real-time operating systems are very costly to develop.
- Real-time operating systems are very complex and can consume critical CPU cycles.
Time-Sharing Operating System
In the Time Sharing operating system, computer resources are allocated in a time-dependent fashion to several programs simultaneously. Thus it helps to provide a large number of user's direct access to the main computer. It is a logical extension of multiprogramming. In time-sharing, the CPU is switched among multiple programs given by different users on a scheduled basis.
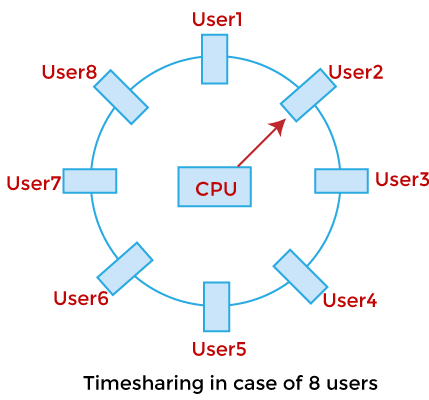
A time-sharing operating system allows many users to be served simultaneously, so sophisticated CPU scheduling schemes and Input/output management are required.
Time-sharing operating systems are very difficult and expensive to build.
Advantages of Time Sharing Operating System
- The time-sharing operating system provides effective utilization and sharing of resources.
- This system reduces CPU idle and response time.
Disadvantages of Time Sharing Operating System
- Data transmission rates are very high in comparison to other methods.
- Security and integrity of user programs loaded in memory and data need to be maintained as many users access the system at the same time.
Distributed Operating System
The Distributed Operating system is not installed on a single machine, it is divided into parts, and these parts are loaded on different machines. A part of the distributed Operating system is installed on each machine to make their communication possible. Distributed Operating systems are much more complex, large, and sophisticated than Network operating systems because they also have to take care of varying networking protocols.
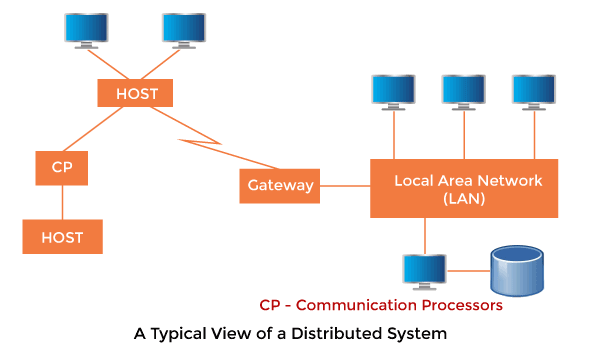
Advantages of Distributed Operating System
- The distributed operating system provides sharing of resources.
- This type of system is fault-tolerant.
Disadvantages of Distributed Operating System
- Protocol overhead can dominate computation cost.
Modern operating systems require hardware support to perform various essential functions. The specific hardware requirements can vary depending on the type and complexity of the operating system, but here are some fundamental hardware support elements necessary for a modern operating system:
-
Processor (CPU): A modern operating system needs to support the processor architecture of the hardware it runs on. It should be able to manage and schedule tasks efficiently across multiple processor cores if the system has a multi-core CPU.
-
Memory (RAM): The operating system needs to be able to manage and allocate system memory (RAM) for running applications and the OS itself. Virtual memory management is also crucial for handling memory paging and swapping.
-
Storage Devices: Operating systems need support for various storage devices, such as hard drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and other storage technologies. This involves device drivers and file system support for managing data storage and retrieval.
-
Input/Output (I/O) Devices: Support for a variety of input and output devices is essential. This includes drivers for peripherals like keyboards, mice, monitors, printers, network interfaces, and other external devices.
-
Interrupt Handling: The operating system must be able to handle hardware interrupts generated by devices. Interrupts are signals that hardware devices send to the CPU to gain its attention.
-
Device Drivers: Device drivers are essential software components that enable the operating system to communicate with and control hardware devices. These drivers act as intermediaries between the operating system's kernel and the hardware.
-
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): For systems with graphical user interfaces (GUIs), support for GPUs is necessary. This includes graphics drivers and APIs for rendering graphics and managing display output.
-
Network Support: Modern operating systems require networking support to enable communication between devices. This involves network drivers, protocols (such as TCP/IP), and networking services.
-
Power Management: Support for power management features, such as sleep, hibernate, and dynamic frequency scaling, is crucial for energy efficiency in laptops and other portable devices.
-
Security Features: Hardware support for security features like hardware-level encryption, secure boot, and Trusted Platform Module (TPM) can enhance the overall security of the system.
-
Clock and Timer Support: The operating system relies on accurate timing information for scheduling tasks and managing system events. Support for system clocks and timers is crucial.
-
BIOS/UEFI Firmware: The operating system interacts with the system's firmware (BIOS or UEFI) during the boot process. Compatibility with the system's firmware is necessary for a successful boot and initialization.
These are general hardware requirements, and the specific details may vary based on the architecture and design of the operating system. Modern operating systems are designed to be versatile and compatible with a wide range of hardware configurations.
Operating System Services
Operating system is a software that acts as an intermediary between the user and computer hardware. It is a program with the help of which we are able to run various applications. It is the one program that is running all the time. Every computer must have an operating system to smoothly execute other programs. The OS coordinates the use of the hardware and application programs for various users. It provides a platform for other application programs to work. The operating system is a set of special programs that run on a computer system that allows it to work properly. It controls input-output devices, execution of programs, managing files, etc.
Program Execution
It is the Operating System that manages how a program is going to be executed. It loads the program into the memory after which it is executed. The order in which they are executed depends on the CPU Scheduling Algorithms. A few are FCFS, SJF, etc. When the program is in execution, the Operating System also handles deadlock i.e. no two processes come for execution at the same time. The Operating System is responsible for the smooth execution of both user and system programs. The Operating System utilizes various resources available for the efficient running of all types of functionalities.
Input Output Operations
Operating System manages the input-output operations and establishes communication between the user and device drivers. Device drivers are software that is associated with hardware that is being managed by the OS so that the sync between the devices works properly. It also provides access to input-output devices to a program when needed.
*Communication between Processes*
The Operating system manages the communication between processes. Communication between processes includes data transfer among them. If the processes are not on the same computer but connected through a computer network, then also their communication is managed by the Operating System itself.
File Management
The operating system helps in managing files also. If a program needs access to a file, it is the operating system that grants access. These permissions include read-only, read-write, etc. It also provides a platform for the user to create, and delete files. The Operating System is responsible for making decisions regarding the storage of all types of data or files, i.e, floppy disk/hard disk/pen drive, etc. The Operating System decides how the data should be manipulated and stored.
Memory Management
Let’s understand memory management by OS in simple way. Imagine a cricket team with limited number of player . The team manager (OS) decide whether the upcoming player will be in playing 11 ,playing 15 or will not be included in team , based on his performance . In the same way, OS first check whether the upcoming program fulfil all requirement to get memory space or not ,if all things good, it checks how much memory space will be sufficient for program and then load the program into memory at certain location. And thus , it prevents program from using unnecessary memory.
Process Management
Let’s understand the process management in unique way. Imagine, our kitchen stove as the (CPU) where all cooking(execution) is really happen and chef as the (OS) who uses kitchen-stove(CPU) to cook different dishes(program). The chef(OS) has to cook different dishes(programs) so he ensure that any particular dish(program) does not take long time(unnecessary time) and all dishes(programs) gets a chance to cooked(execution) .The chef(OS) basically scheduled time for all dishes(programs) to run kitchen(all the system) smoothly and thus cooked(execute) all the different dishes(programs) efficiently.
Secuirity and Privacy
-
*Secuirity :* OS keep our computer safe from an unauthorised user by adding secuirity layer to it.Basically, Secuirity is nothing but just a layer of protection which protect computer from bad guys like viruses and hackers. OS provide us defenses like firewalls and anti-virus software and ensure good safety of computer and personal information.
-
*Privacy :* OS give us facility to keep our essential information hidden like having a lock on our door, where only you can enter and other are not allowed . Basically , it respect our secrets and provide us facility to keep it safe.
Resource Management
System resources are shared between various processes. It is the Operating system that manages resource sharing. It also manages the CPU time among processes using CPU Scheduling Algorithms. It also helps in the memory management of the system. It also controls input-output devices. The OS also ensures the proper use of all the resources available by deciding which resource to be used by whom.
User Interface
User interface is essential and all operating systems provide it. Users either interface with the operating system through the command-line interface or graphical user interface or GUI. The command interpreter executes the next user-specified command.
A GUI offers the user a mouse-based window and menu system as an interface.
Networking
This service enables communication between devices on a network, such as connecting to the internet, sending and receiving data packets, and managing network connections.
Error Handling
The Operating System also handles the error occurring in the CPU, in Input-Output devices, etc. It also ensures that an error does not occur frequently and fixes the errors. It also prevents the process from coming to a deadlock. It also looks for any type of error or bugs that can occur while any task. The well-secured OS sometimes also acts as a countermeasure for preventing any sort of breach of the Computer System from any external source and probably handling them.
Time Management
Imagine traffic light as (OS), which indicates all the cars(programs) whether it should be stop(red)=>(simple queue) , start(yellow)=>(ready queue),move(green)=>(under execution) and this light (control) changes after a certain interval of time at each side of the road(computer system) so that the cars(program) from all side of road move smoothly without traffic.
What is a system program?
In an operating system a user is able to use different types of system programs and the system program is responsible for all the application software performance of the computer.
The system programs are responsible for the development and execution of a program and they can be used by the help of system calls because system calls define different types of system programs for different tasks.
-
File management − These programs create, delete, copy, rename, print, exit and generally manipulate the files and directory.
-
Status information − It is the information regarding input, output process, storage and the CPU utilization time how the process will be calculated in how much memory required to perform a task is known by status information.
-
Programming language supports − compiler, assembler, interrupt are programming language support used in the operating system for a particular purpose in the computer.
-
Programming Loading and execution − The needs to enter the program and after the loading of a program it needs to execute the output of the programs and this task is also performed by system calls by the help of system programs.
-
Communication − These services are provided by the user because by using this number of devices communicates with each other by the help of device or wireless and communication is necessary for the operating system.
-
Background services − There are different types of services available on the operating system for communication and background service is used to change the background of your window and it also works for scanning and detecting viruses in the computer.
Purpose of using system program
System programs communicate and coordinate the activities and functions of hardware and software of a system and also controls the operations of the hardware. An operating system is one of the examples of system software. Operating system controls the computer hardware and acts like an interface between the application software’s.
Introduction of System Call
In computing, a *system call is a programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the kernel of the operating system it is executed on. A system call is a way for programs to interact with the operating system. A computer program makes a system call when it makes a request to the operating system’s kernel. System call provides* the services of the operating system to the user programs via Application Program Interface(API). It provides an interface between a process and an operating system to allow user-level processes to request services of the operating system. System calls are the only entry points into the kernel system. All programs needing resources must use system calls.
A user program can interact with the operating system using a system call. A number of services are requested by the program, and the OS responds by launching a number of systems calls to fulfill the request. A system call can be written in high-level languages like C or Pascal or in assembly language. If a high-level language is used, the operating system may directly invoke system calls, which are predefined functions.
A system call is a mechanism used by programs to request services from the operating system (OS). In simpler terms, it is a way for a program to interact with the underlying system, such as accessing hardware resources or performing privileged operations.
A system call is initiated by the program executing a specific instruction, which triggers a switch to kernel mode, allowing the program to request a service from the OS. The OS then handles the request, performs the necessary operations, and returns the result back to the program.
System calls are essential for the proper functioning of an operating system, as they provide a standardized way for programs to access system resources. Without system calls, each program would need to implement its own methods for accessing hardware and system services, leading to inconsistent and error-prone behavior.
*Services Provided by System Calls*
- Process creation and management
- Main memory management
- File Access, Directory, and File system management
- Device handling(I/O)
- Protection
- Networking, etc.
- *Process control:* end, abort, create, terminate, allocate, and free memory.
- *File management:* create, open, close, delete, read files,s, etc.
- *Device management*
- *Information maintenance*
- *Communication*
Features of System Calls
- *Interface:* System calls provide a well-defined interface between user programs and the operating system. Programs make requests by calling specific functions, and the operating system responds by executing the requested service and returning a result.
- *Protection:* System calls are used to access privileged operations that are not available to normal user programs. The operating system uses this privilege to protect the system from malicious or unauthorized access.
- *Kernel Mode:* When a system call is made, the program is temporarily switched from user mode to kernel mode. In kernel mode, the program has access to all system resources, including hardware, memory, and other processes.
- *Context Switching:* A system call requires a context switch, which involves saving the state of the current process and switching to the kernel mode to execute the requested service. This can introduce overhead, which can impact system performance.
- *Error Handling:* System calls can return error codes to indicate problems with the requested service. Programs must check for these errors and handle them appropriately.
- *Synchronization:* System calls can be used to synchronize access to shared resources, such as files or network connections. The operating system provides synchronization mechanisms, such as locks or semaphores, to ensure that multiple programs can access these resources safely.
Design approaches in Operating System
The operating system may be implemented with the assistance of several structures. The structure of the operating system is mostly determined by how the many common components of the OS are integrated and merged into the kernel. In this article, you will learn the following structure of the OS. Various structures are used in the design of the operating system. These structures are as follows:
- Simple Structure
- Micro-Kernel Structure
- Layered Structure
Simple Structure
Such OS's are small, simple, and limited, with no well-defined structure. There is a lack of separation between the interfaces and levels of functionality. The MS-DOS is the best example of such an operating system. Application programs in MS-DOS can access basic I/O functions. If one of the user programs fails on these OSs, the complete system crashes. Below is the diagram of the MS-DOS structure that may help you understand the simple structure.
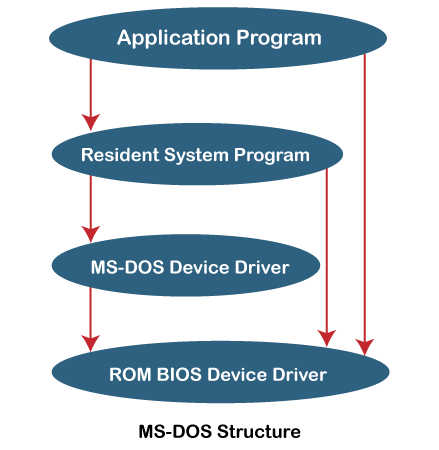
Advantages and Disadvantages of Simple Structure
There are various advantages and disadvantages of the Simple Structure. Some advantages and disadvantages of the Simple Structure are as follows:
Advantages
- It provides superior application performance due to the limited interfaces between the application program and the hardware.
- It is simple for kernel developers to create such an operating system.
Disadvantages
- The structure is quite complex because there are no apparent boundaries between modules.
- It does not impose data concealment in the operating system.
Micro-Kernel Structure
This micro-kernel structure creates the OS by eliminating all non-essential kernel components and implementing them as user programs and systems. Therefore, a smaller kernel is known as a micro-kernel.
The benefits of this micro-kernel structure are that all new services must be added to userspace rather than the kernel, and the kernel does not require to be updated. Therefore, it is more secure and trustworthy. If a service fails, the remainder of the OS is unaffected. Mac OS is the best instance of this type of operating system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro-Kernel Structure
There are various advantages and disadvantages of the Micro-Kernel Structure. Some advantages and disadvantages of the Micro-Kernel Structure are as follows:
Advantages
- It allows the OS to be portable across platforms.
- They can be effectively tested because the microkernels are small.
Disadvantages
- The performance of the system suffers as the level of inter-module communication rises.
Layered Structure
An operating system can be divided into sections while retaining far more control over the system. The OS is divided into layers in this arrangement (levels). The hardware is on the bottom layer (layer 0), and the user interface is on the top layer (layer N). These layers are designed in such a way that each layer only requires the functions of the lower-level layers. Debugging is simplified because if lower-level layers are debugged, and an error occurs during debugging, the error must occur only on that layer. The lower-level layers have been thoroughly tested.
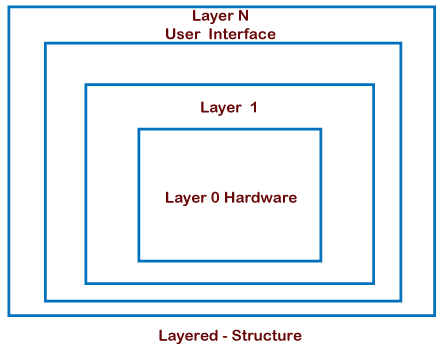
UNIX is the best example of the Layered Structure. The main disadvantage of this structure is that data must be updated and sent on to each layer, which adds overhead to the system. Furthermore, careful planning of the layers is required because a layer may use only lower-level layers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Layered Structure
There are various advantages and disadvantages of the Layered Structure. Some advantages and disadvantages of the Layered Structure are as follows:
Advantages
- Layering makes it easier to improve the OS as the implementation of a layer may be changed easily without affecting the other layers.
- Debugging and system verification are simple to carry out.
Disadvantages
- When compared to a simple structure, this structure degrades application performance.
- It needs better planning to construct the layers because higher layers only utilize the functionalities of lower layers.
Modular structure or approach
It is regarded as the best approach for an operating system. It involves designing a modular kernel. It is comparable to a layered structure in that each kernel has specified and protected interfaces, but it is more flexible because a module may call any other module. The kernel contains only a limited number of basic components, and extra services are added to the kernel as dynamically loadable modules either during runtime or at boot time.
References
https://www.javatpoint.com/types-of-operating-systems https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/evolution-of-operating-system/ https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-is-the-operating-system-evolution https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/operating-system-services/ https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-is-a-system-program https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-of-system-call/ https://www.javatpoint.com/design-approaches-in-operating-system